At Cotwall End Primary School, we adhere to the 2014 National Curriculum, which provides a comprehensive framework for our teaching. We have developed our own mid-term plans, specifically tailored to the diverse needs of our children. This personalised approach ensures that each pupil is afforded the opportunity to experience coverage and progression in their educational journey.
Recognising the vital role that parental involvement plays in a child's education, we actively encourage parents to support their child's mathematical development. We promote the importance of home learning and urge families to engage with the tasks set, as this partnership can significantly enhance a child's confidence and competence in mathematics. We appreciate the continued collaboration with parents and guardians, which further enriches our students’ learning experiences, enabling them to thrive in their academic pursuits. Your support is invaluable in nurturing a positive attitude towards mathematics.

524 x 2= 848 ÷ 4= 3254 + 1423= 4346 - 2224=

Concrete | Pictoral | Abstract |
|---|---|---|
Children should have the opportunity to work with physical objects/concrete resources, in order to bring the maths to life and to build understanding of what they are doing.
Alongside concrete resources, children should work with pictoral representations, making links to the concrete. Visualising a problem in this way can help children to reason and to solve problems.
With the support of both the concrete and pictorial representations, children can develop their understanding of abstract methods.
The Aims of Mathematics Curriculum at Cotwall End
-
To ensure consistency and progression in our approach to calculation and enable a smooth transition between year groups and phases.
-
To ensure that all mathematics is taught through the process of:
Concrete Pictorial Abstract.
What is the CPA Approach?
-
To ensure that pupils are competent in fluency, reasoning and problem solving and can make informed and appropriate choices about the methods they wish to use.
White Rose Maths
Click on the link below to view the Ready to Progress Document for each year group.
NEW NC RTP 2022.3 FINAL March 2023 version.pdf (whiteroseeducation.com)
If you want to know more about White Rose Maths, follow the link below.
Advice and guidance for parents | White Rose Maths (whiteroseeducation.com)
A Typical Lesson
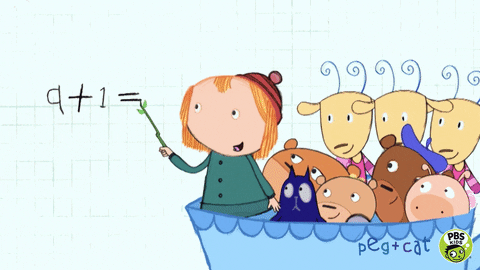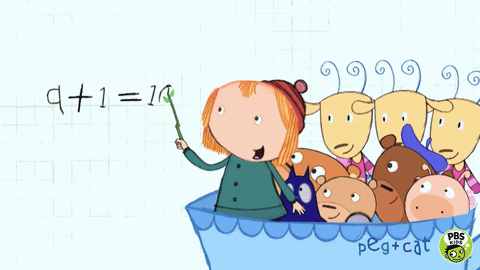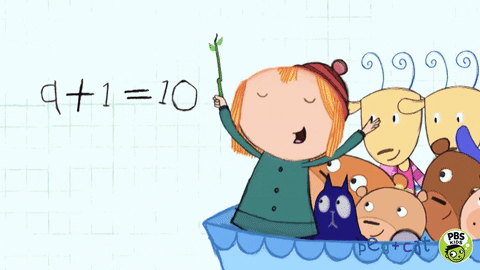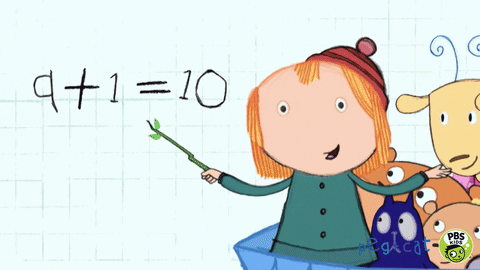
We understand that revisiting learning deepens understanding while reinforcing knowledge, concepts, and procedures. From Year 1- 6 children start the lesson with a fluency task which revisits the children’s knowledge of number. Reception also begin with a fluency task once they have been taught the concepts after Autumn half term. By the summer term they can tackle 3 questions based on previous learning. Children tackle questions based on the 4 operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. One other aspect of mathematics will also be introduced based on the current lessons, such as: fractions or measures. Fluency takes 10 minutes and teachers model the correct written calculations.
An example of Year 1 Fluency
An example of Year 4 Fluency
Maths Gallery
Look at our fabulous displays and maths work from each year group to see how much we enjoy maths at Cotwall End.
Fluency: 8 +__ = 20
20 - 16 = __
Share 20 eyes between 10 monsters.
How many eyes does each monster have? ____
7 groups of 10 is ___
How many?
___ tens
___ ones
___ altogether
Compare Mass
Count and recognise numbers
Reception
Children learn about mass. Here they use balance scales to compare the weight of an object by counting cubes.
The children also enjoy using different equipment to count and make a particular amount. The use of numicon equipment can help a child to recognise, count and make a number.




Fact Families
Addition Sentences
Year 1
Year 1 can use part whole models and double-sided counters to write addition facts.



Count in 3s
Bonds to 10
Year 2
Children can reason about counting in 3s and use number tracks to help them. They revisit and consolidate learming from year 1 by using multilink equipment to create number bonds to 10 and draw their own part- whole models to show number facts.




Making Connections
Year 3
Children make connections between calculations. For example, if children know 5 + 7 = 12, then they also know that 12 – 5 = 7, 120 – 50 = 70 and 50 + 70 = 120. They can use part- whole models and place value charts to show this.



Estimate on a number line to 10 000
Roman Numerals
Year 4
Children can work out the value of each interval to estimate missing number up to 10 000. The children also build on their knowledge of Roman Numerals from 1-12 on a clock face to know numbers up to 100.



Solve multi-step problems with numbers more than 4 digits.
Year 5
Children use the strategies they have learned so far to solve problems with more than one step.


Calculations
Year 6
Children learn to perfect formal calculations across all four operations deciding which method is most appropriate.



Maths Day